Characteristics of X-linked Recessive Disorders Include Which of the Following
Assume X is normal X1 is recessive for the trait and Y is normal. Red-green color blindness simply means that a person cannot distinguish shades of red and green usually blue-green.
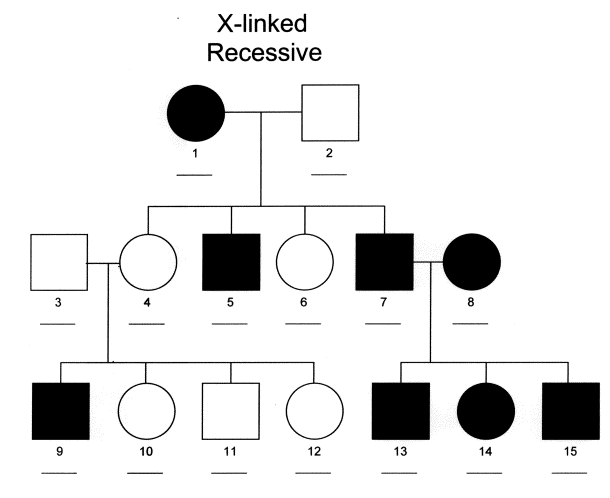
Sex X Linked Recessive Inheritance Michigan Genetics Resource Center
In genetic males who have only one X chromosome one altered copy of the gene in each cell is sufficient to cause the condition.

. Males have only one X chromosome. This condition is inherited in an X-linked recessive pattern. Hepatology communications 42 157-171.
The most common X-linked recessive disorders are. A characteristic of X-linked inheritance is that fathers cannot pass X-linked traits to their sons no male-to-male transmission. OMIM Phenotypic Series 607594 is characterized by humoral immune deficiency with onset after age 24 months and usually in young adulthood resulting in increased susceptibility to infections and diminished responses.
And symptoms of anemia. Gene found on the X chromosome that codes for dystrophin. In males who have only one X.
Hemophilia A is a classic X-linked recessive disorder in which the blood fails to clot normally because of a deficiency of factor VIII a protein in the clotting cascade Case 21. 1 5 Dysgammaglobulinemia causes an increased risk of recurrent infections. Its commonness may be explained by its relatively benign nature.
The WAS protein WASp is involved in signal transduction and also is known to regulate actin filament assembly. 3 XLP1 is caused by mutations in the SH2D1A gene and XLP2 is caused by mutations in the XIAP gene. Question 14 An autosomal recessive disorder such as cystic fibrosis is expressed in.
Examples of X-linked recessive conditions include red-green color blindness and hemophilia A. It is also known as daltonism. B Boys and girls are equally affected.
FMD1 Frontometaphyseal dysplasia MLPA GTR Test ID Help Each Test is a specific orderable test from a particular laboratory and is assigned a unique GTR accession number. Boys and girls are equally affected. Question 1 An example of an X-linked recessive condition or trait is a.
However the Y chromosome doesnt contain most of the genes of the X chromosome. Males and females are equally affected. X-linked recessive diseases most often occur in males.
Redgreen color blindness a very common trait in humans and frequently used to explain X-linked disorders. The differential diagnosis of X-linked lymphoproliferative disease XLP includes the following. View Notes - Patho Ch 6pdf from MCELLBI 101 at University of California Berkeley.
Heterozygous female are those who are having mutant allele on one X chromosome and normal allele on another X. A condition is considered X-linked if the mutated gene that causes the disorder is located on the X chromosome one of the two sex chromosomes in each cell. Mononucleosis may cause fatigue.
Sickle cell anemia b. Common variable immunodeficiency CVID. Red-green color blindness shows X-linked recessive inheritance.
Affected fathers transmit the gene to all of their sons C. The hereditary nature of hemophilia and even its pattern of transmission have been recognized since ancient times and the condition became known as the royal hemophilia because of its occurrence. Dominant means that a single copy of the mutated gene from one parent is enough to cause the disorder.
Enlarged lymph nodes liver and spleen. X-linked recessive disorders are also caused by variants in genes on the X chromosome. Characteristics of X-linked recessive disorders include which of the following.
Autosomal means that the gene in question is located on one of the numbered or non-sex chromosomes. Heterozygous female may have a variable expression of X linked recessive disorder due to the random process of X inactivation involving inactivation of the X chromosome with a mutant allele in some cells while. Characteristics of X-linked recessive disorders include which of the following.
All daughters of affected fathers are carriers. They are then replaced by connective tissue and fat in the muscle. All daughters of affected fathers are carriers B.
These are related X-linked recessive disorders caused by a defect in the Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome gene characterized by immunodeficiency recurrent infections eczema and thrombocytopenia with small platelets and a platelet SPD. Heterozygous female are those who are having mutant allele on one X chromosome and normal allele on another X. Which of the following is an example of an X-linked recessive disorder.
These individuals lack and so their poorly anchored muscle cells are torn apart during muscle contraction. Between seven and ten percent of men and 049 to 1 of women are affected. Most pedigrees showing the hypothetical human trait show the following characteristics.
Frontometaphyseal dysplasia 1 305620 X-linked recessive. A child of a person affected by an. The clinical manifestations occur early in infancy and the disease course is usually nonprogressive.
An inflamed and sore throat. Lucy does not need. Virologic and immunologic characteristics.
Their visual acuity ability to. Because of that it doesnt protect the male. Then an individual with the.
It is an autosomal recessive or X-linked disorder of the cone photoreceptors characterized by inability to distinguish colors severely impaired visual acuity photophobia and nystagmus. The Y chromosome is the other half of the XY gene pair in the male. A single recessive gene on that X chromosome will cause the disease.
This causes the cells to swell and die. Females may experience less severe symptoms of the disorder than males. Heterozygous female may have a variable expression of X linked recessive disorder due to the random process of X inactivation involving inactivation of the X chromosome with a mutant allele in some cells while.
Hepatitis B and pregnancy. Autosomal dominant is a pattern of inheritance characteristic of some genetic disorders. The format is GTR000000011 with a leading prefix GTR followed by 8 digits a period then 1 or more digits representing the version.
A sex-linked recessive disorder e. An affected man often has phenotypically normal parents. The son of a carrier mother has a 25 chance of being affected D.
A All daughters of affected fathers are carriers. Which of the following statements is incorrect concerning an X-linked recessive trait in humans. Genetic and Developmental Disorders Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE.
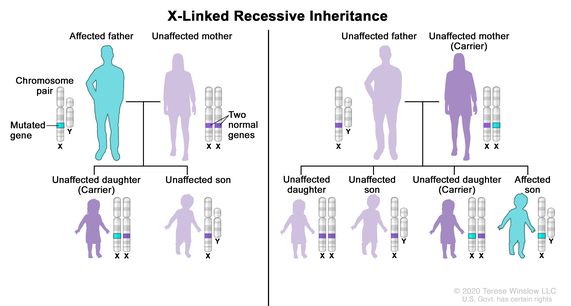
Definition Of X Linked Recessive Inheritance Nci Dictionary Of Genetics Terms Nci

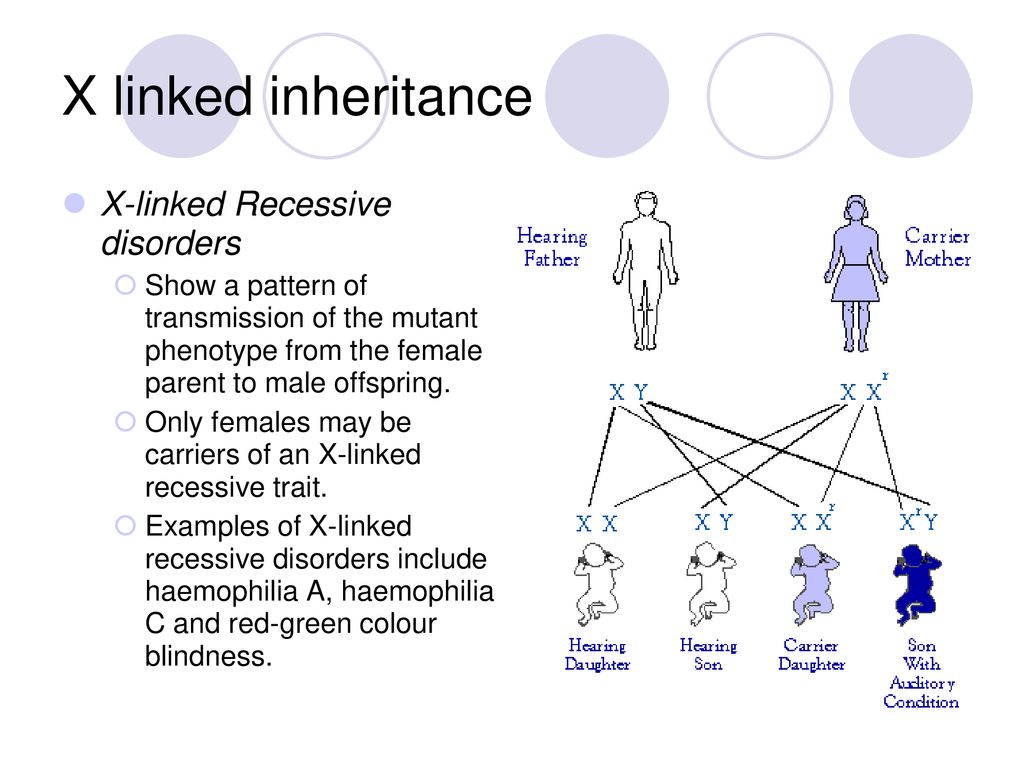
No comments for "Characteristics of X-linked Recessive Disorders Include Which of the Following"
Post a Comment